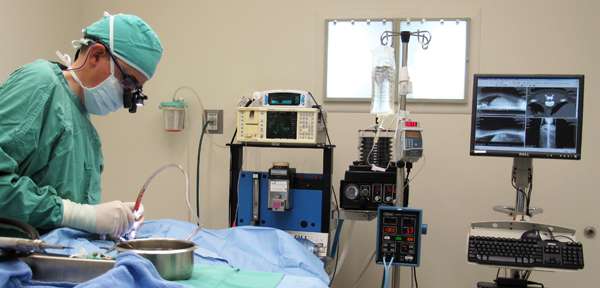
General anesthesia is necessary for many medical procedures and with modern methods of anesthesia administration and monitoring, the risk in veterinary medicine is minimized as in human medicine. General anesthetic agents cause overall central nervous system effects producing reversible unconciousness and analgesia. They also affect the body’s homeostatic mechanisms and therefore the patient’s condition must be managed to keep the body functioning in equilibrium.
At the Veterinary Neurological Center, the doctors and technicians take numerous measures to ensure every patient is anesthetized as safely as possible. Prior to inducing a patient the doctors consider many factors such as patient history, physical examination findings and labwork results. During the anesthetic procedure, specially trained technicians closely monitor parameters such as breathing, circulation and temperature and control them as needed. Monitoring equipment (see below) is used to augment clinical observations (e.g. palpating pulse) and is necessary because: 1) they can easily and accurately detect complex vital signs of patients 2) they free up hands so anyone can see the current (and recent) measurements 3) they allow many parameters to be monitored simultaneously. ►Click here to learn more about anesthesia and monitoring.
Some Key Side Effects of General Anesthetic Agents:
- CNS depression
- depression of body temperature regulating centers (hypothalamus)
- increased cerebral blood flow
- respiratory depression
- hypotension
- vasodilation
- myocardial depression
- muscular relaxation
MECHANISMS & TECHNIQUES USED TO MONITOR & CONTROL THE BODY’S SYSTEMS:
Tidal Volume and Respiratory Rate
- Ventilator
- Clinical Observations: chest (and abdominal) movements
Oxygen Saturation (and heart rate)
- Pulse Oximeter
- Clinical Observations: mucus membrane color, capillary refill time
Expired Carbon Dioxide (and respiratory rate)
- Capnograph
- Clinical Observations: mucus membrane/tongue color
Anesthetic Concentration
- Agent Analyzer
- Clinical Observations: menace response, reflexes (palpebral, corneal, toe pinch), muscle tone
Effects of Anesthesia on the Respiratory System
During breathing, a volume of air is inhaled through the airways (nose/mouth>trachea>bronchi>bronchioles) into millions of tiny gas exchange sacs (the alveoli) deep within the lungs. Oxygen (O2) diffuses into the blood cells from the capillaries of the alveoli where it is circulated to the body’s cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide (CO2), a waste product, is released back into the lungs from the veins. CO2 is a main stimulus for respiration. As the amount of CO2 in the cells increases, the body is triggered to breath to rid the CO2 and intake fresh oxygen that the body’s cells require. An excessive prolonged buildup of CO2 can be toxic to the body primarily because it takes up room in the cells for oxygen.
General anesthetics cause depression of the respiratory center in the brain reducing the ability for patients to breath on their own. Therefore, anesthetic machines are used to breath for patients and they must produce enough gas exchange (ventilation) to keep the patient alive. Ventilation is expressed as the volume of gas inhaled/exhaled during a breath (tidal volume) x the breathing rate. Respiration has two phases: inhalation (oxygenation) measured by pulse oximetry and exhalation measured by capnography. These parameters, along with anesthetic agent concentration, must be monitored closely to ensure proper ventilation.
Electroactivity of the Heart and Heart Rate/Rhythm
- Electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG)
- Clinical Observations: palpate pulse rate, listen to heart with stethoscope
Blood Pressure (and heart rate)
- Blood Pressure Monitor
- Clinical Observations: palpate pulse pressure (and rate)
Blood Flow (and heart rate)
- Doppler
- Clinical Observations: palpate pulse pressure (and rate)
Effects of Anesthesia on the Circulatory System
Proper functioning of the heart and blood vessels is necessary to pump oxygen-rich blood through arteries, arterioles, and capillaries to be utilized by the cells within the body’s tissues. On its way back to the heart, the oxygen-poor blood travels through a system of veins. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, is removed from the blood and replaced with fresh oxygen that has been inhaled through the lungs.
Anesthetic agents depress the heart muscle and vasculature, decreasing cardiac output and blood pressure. Fluid requirements are increased because of fluid loss due to breathing dry, cold oxygen, hemorrhage or exposure of moist viscera to room air (e.g. during surgery). Several measures can be taken to control heart rate, blood pressure and minimize the effects of dehydration, including the administration of certain drugs and intravenous fluids, adjusting the depth of anesthesia, etc. Patients must be monitored closely to ensure the heart is beating properly. A disruption in the flow of blood through the circulatory system could cause a lack of oxygen perfusion that could result in tissue and organ damage.
Core Body Temperature
- Thermometer
Effects of Anesthesia on Thermoregulation
Cells and tissues function and communicate well at a normal body temperature. Patients frequently become hypothermic during anesthesia because of inhalation of cold gasses, exposure of body cavities to the room air (e.g. during surgery), and loss of normal thermoregulatory mechanisms and behaviors. Hypothermia leads to depression of all physiologic functions (including respiration and cardiac function) and slows the metabolism of anesthetics resulting in prolonged recovery times. Heat loss is prevented by minimizing anesthetic times, insulating cold surfaces with blankets and supplementing heat with water-driven heating pads, pre-warmed fluids and/or warm air blowers (BEHR Huggers).
